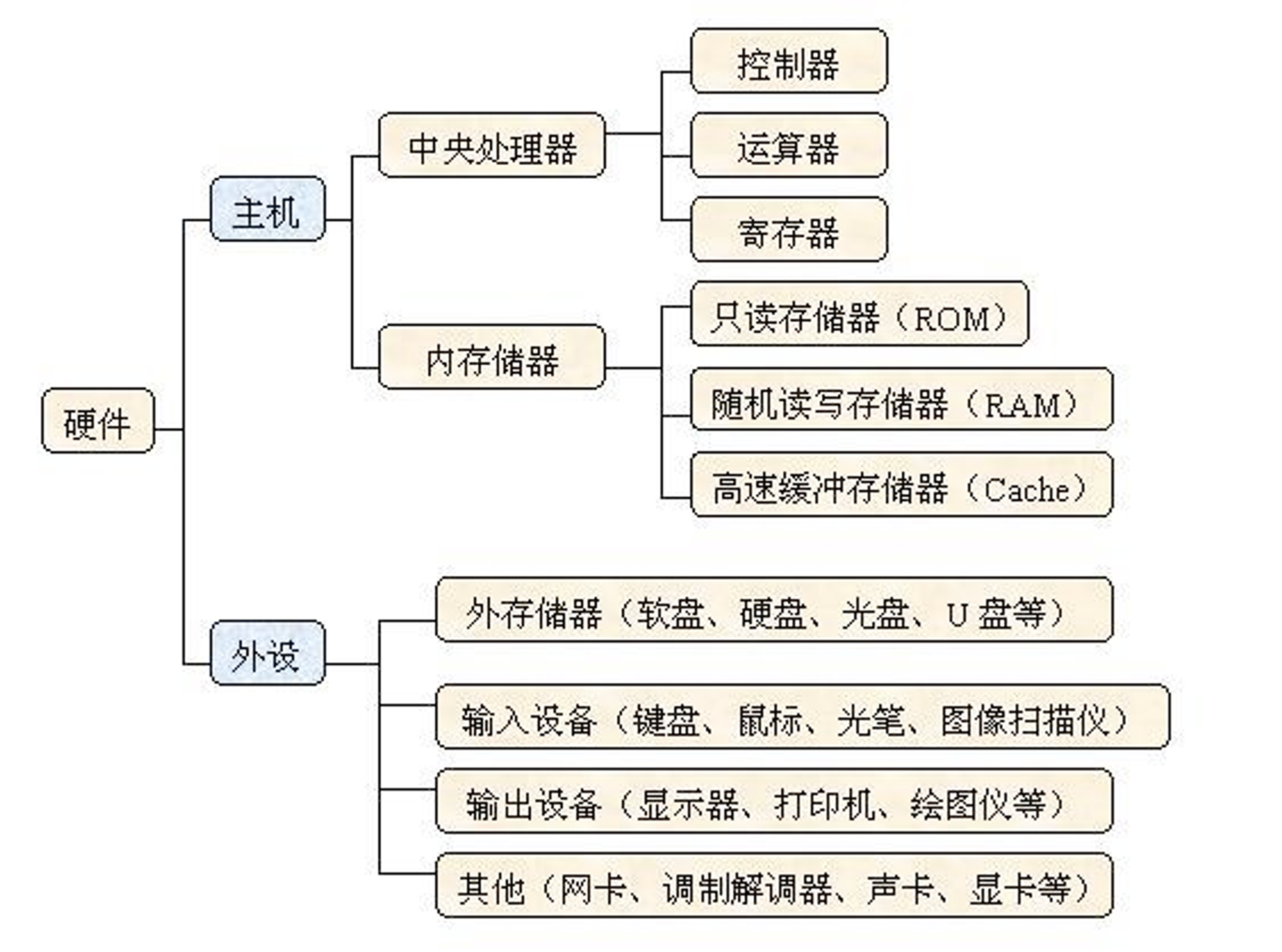
File & I/O
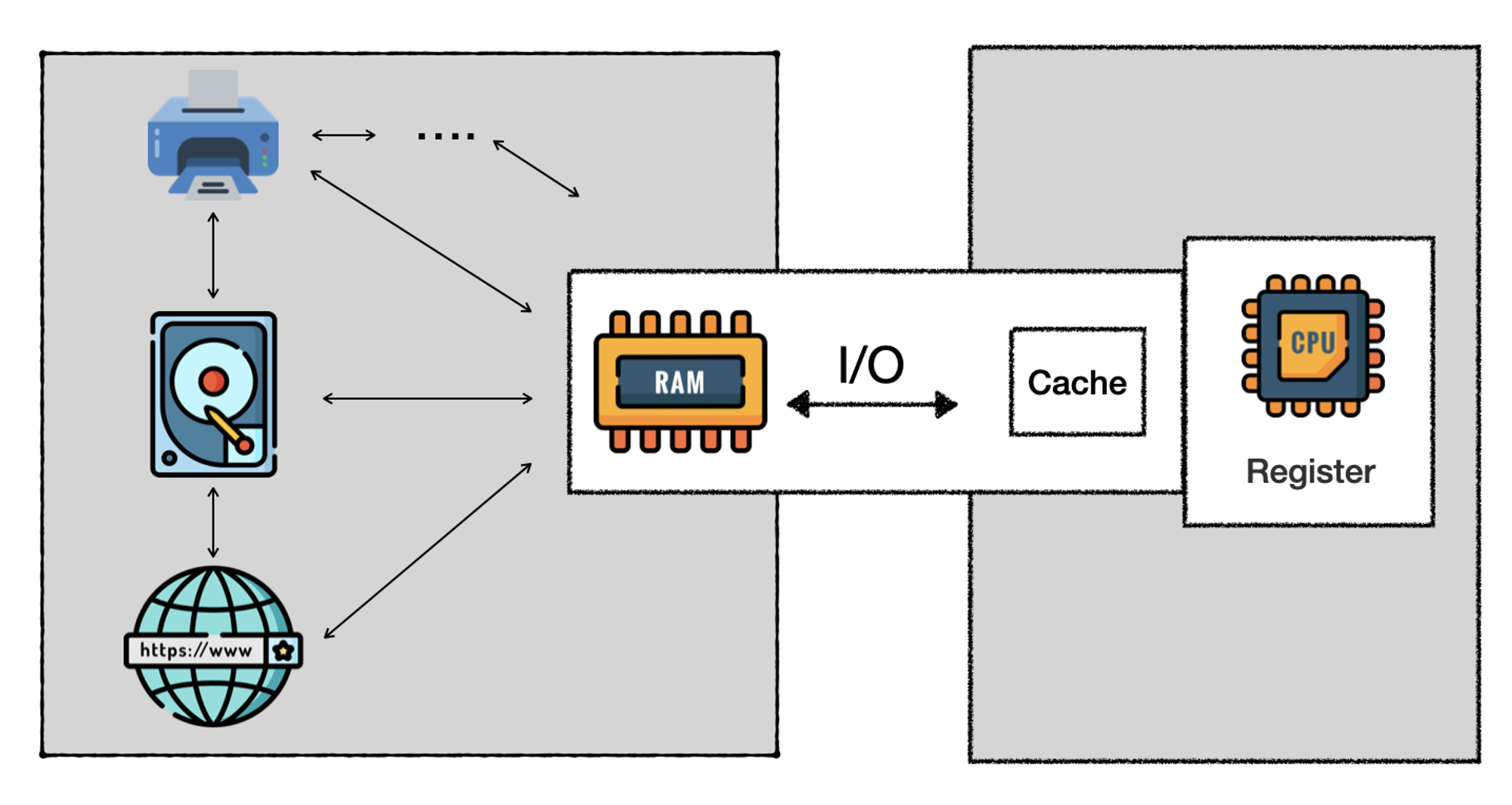
What is I/O?
处理器访问任何寄存器和Cache等封装以外的数据资源都可以当成 I/O 操作,包括内存,磁盘,显卡等外部设备或者网络。
Why do you we non-volatile storage?
- store data after powering off your computer
- store a large mount of data for reuse
- share data among programs
What is streaming?
- build a pipeline to send data in and out
- python use streaming by
default
python
file = open(...) # file is a streaming object, it is the pipline between code and the target file
pipeline = open(...) # makes more senseData Types of I/O
You can only read/write
textorbinarydata from/into file.
- Text I/O: for
textdata
python
f = open("myfile.txt", "rt")- Binary I/O: for
binarydata,buffered: music, video
python
f = open("myfile.jpg", "rb")Buffered and UnBuffered I/O
- send a chunk of data rather than a piece of data
- Raw I/O: for
binarydata, notbuffered, rarely use
python
f = open("myfile.jpg", "rb", buffering=0)Input: Read
r: Read. Default value- read data from the flie if the file exists
- error if the file does
notexist
pythonfile = open("words.txt", "r") file = open("not-exist.txt") # throw error- how to read
pythononeline = file.readline() # read one line lines = file.readlines() # store each line in an array [l1,l2,l3...ln] content = file.read() # read all content once f5 = file.readline(5) # read first 4 characters of the current line f5 = file.read(5) # read first 5 characters of all content for line in file: # for loop print(line) next(file) # iterator method- manipulate the
cursor(offset)
python# every time you run read txt file using any of above functionalities, the cursor will move downwards. # words.txt: # -> 1 | # 2 | # ↓ file.open('words.txt') # cursor at 0 file.readline() # 1 file.readline() # 2 file.readline # nothing! file.seek(0) # move curosr back to top file.tell() # print the current position of the cursor- It's
not requiredto close the I/O if you are only reading data. But it isrecommended.
pythonfile.close()- If you want to
auto closethe file
pythonwith open('words.txt') as file: # your read actions here # you don't have to add file.close() any more
Output: Create, Write, Append
a: Append.- create the file if the file does
notexist - adding data at the end of the file if the file already exists
pythonfile = open("words.txt","a") file = open("not-exist.txt","a") # will automatically create not-exist.txt in current path- create the file if the file does
w: Write.- create the file if the file does
notexist. - clear content of an existing file and add data at the head of the file
pythonfile.open("words.txt","w") # no error file.open("not-exist.txt","w") # will automatically create nont-exist.txt in current path- create the file if the file does
x: Create- create the file if it does
notexist errorif the file already exists
pythonfile.open("file_to_create.txt","x") # will automatically create the file file.open("words.txt","x") # will throw error if the file already exsits- create the file if it does
how to write data
pythonfile = open('words',"a") file.write("hello world") # without newline file.write("hello \n world") # with newline file.write(str(1)) # convert to string before writing number into file file.writeline("hello") # error, no methods for writeline file.writelines(["hello","world"]) # write any array into fileIt is required to use
closeto save data to filewrite()method only writes data into buffer, which is a temporay space in memory. The data will only be store into hard disk(flushing) only after you runclose()pythonfile.close()It is very convenient and recommended to use
withto auto close the filepythonwith open('words.txt') as file: # your writing action here # you don't have to add file.close() any more
Input/output Mode (Not Recommended)
Try to avoid the use of
+
- make readable
pipelinewritable, but behaveweiredto write
python
file = open('words.txt','r+')
# replace different content from top to bottom, if exists, nothing happens
file.write('add something') # no error
file.close()- make appendable
pipelinereadable, but behaveweiredto read
python
file = open('words.txt','a+')
file.read() # nothing showed since cursor will be automatically moved to the bottom
file.write('line\m') # append to the end
file.close()- make writable/creatable
pipelinereadable
python
file = open('words.txt','w+')
file.read() # no error but no content
file.close()Summary

- Basic Syntax
python
pipeline = open('words.txt','rt+')- Auto-close Syntax
python
with open('words.txt','rt') as pipeline:
# actions