Program vs Process vs Thread
Program
the code stored on your computer disk or non-volatile memory to fulfill a certain task. Including System Programs and Application Programs.
- Program will be compiled or programmed to binary in memory before executing it.
Process
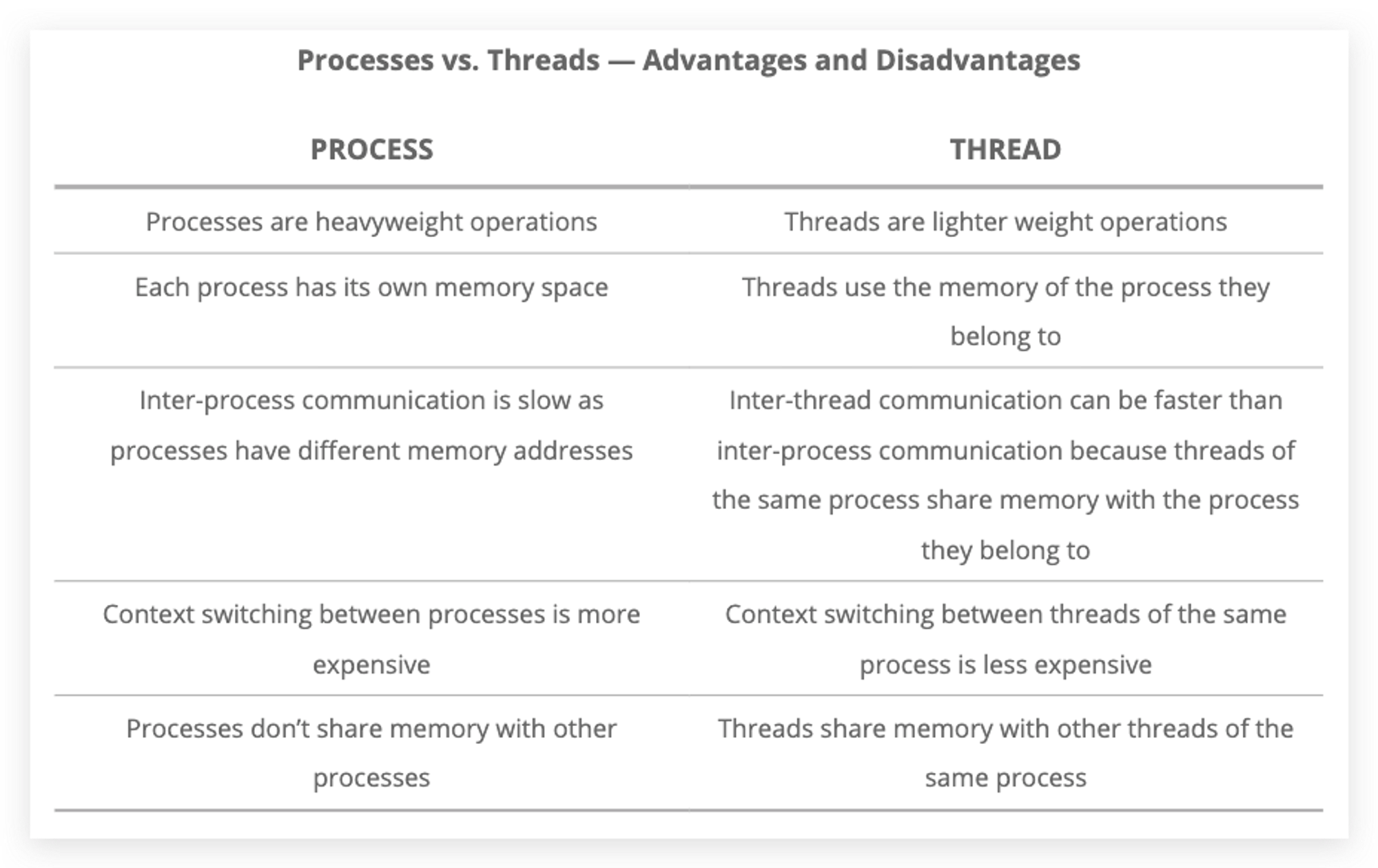
An instance of program that has been loaded into memory along with all the resources needed to operate. A unit for resource allocation
- The Operating System handles the task managing the resources needed to turn program into processes.
- Resources includes:
- register: some part of CPU to store
binary - program counter: special
registerin CPU to do counter work - stack: data structure to store local and small things in memory, managed automatically.
- heap: data structure to store global and big things in memory, managed manually or by Garbage Collection.
- register: some part of CPU to store
- Features:
- One
programmay be associated with manyprocesses. - Independent
Memory Address Space. Inter-communicationis expensive.Robust: One failed won't cause another to fail.
- One
Thread
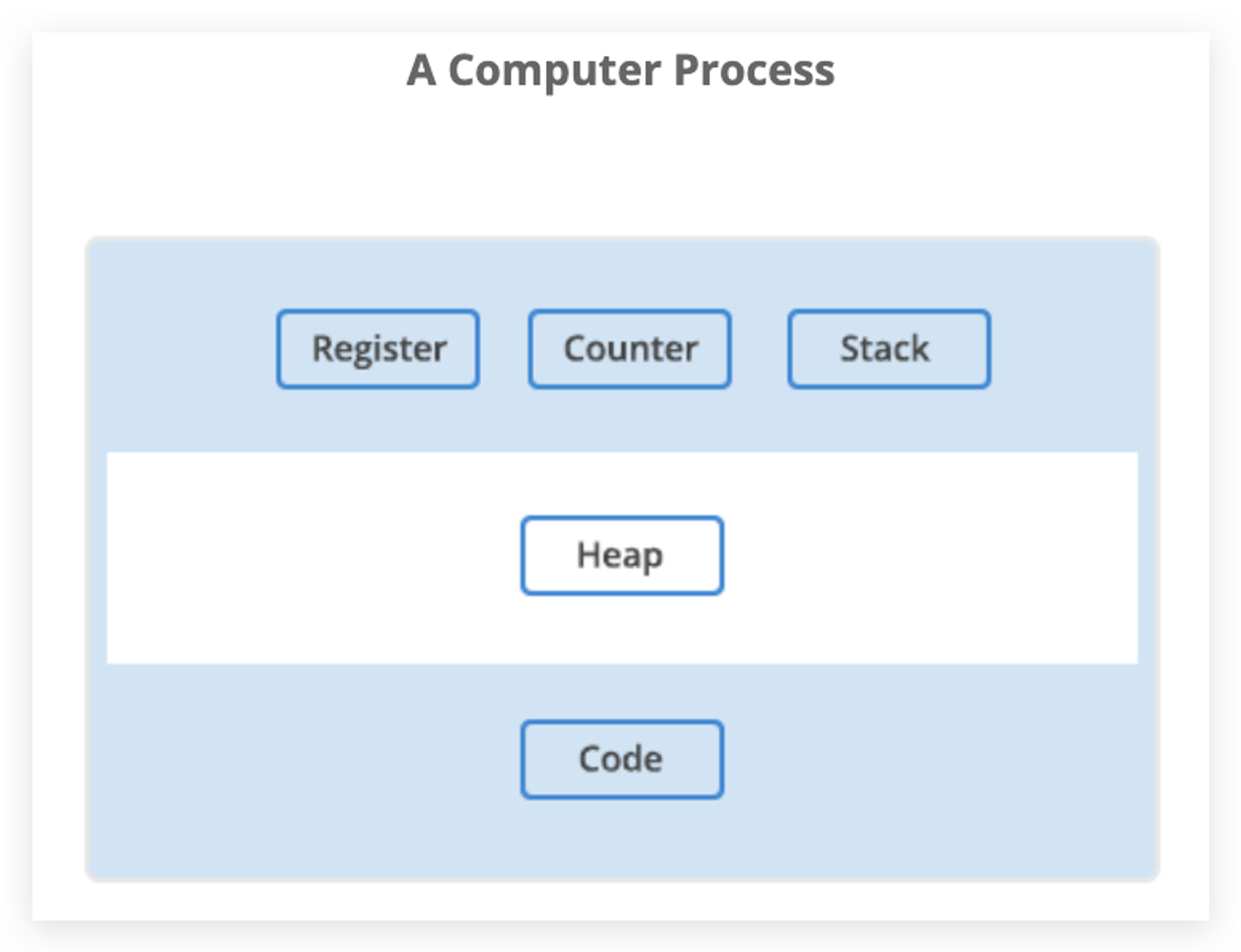
A unit of execution within a process. One process can have one up to many threads. A unit to be scheduled and executed by OS
- Features:
- Share the same
heapin a process - Share the same
codein a process - Has independent
registers - Has independent
stacks - Inter-communication is less expensive
- Vulnerable: one fail can cause another to fail in the same process.
- Share the same
Summary
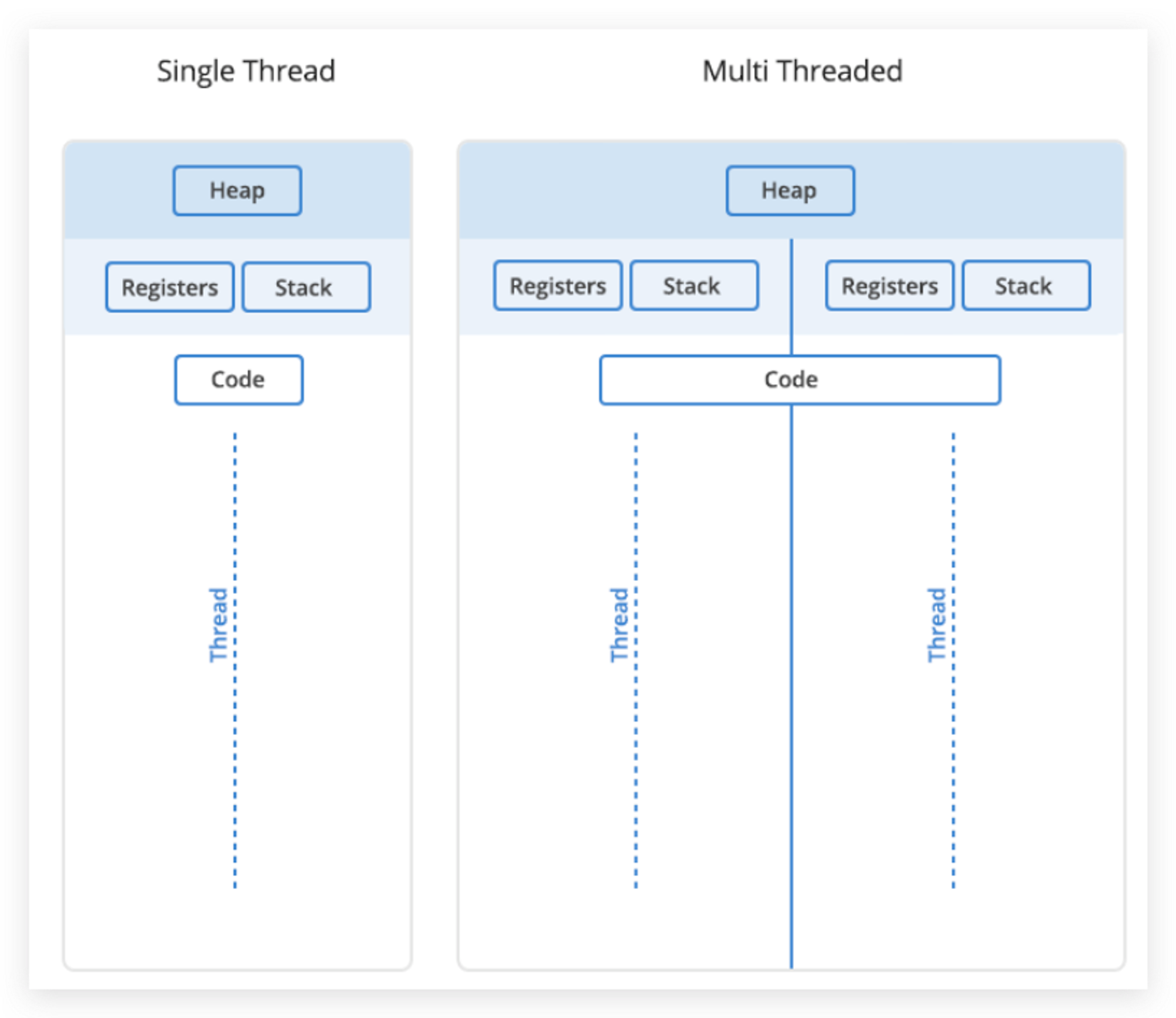
- The program starts out as a
textfile of programming code. - The program is
compiledorinterpretedinto binary form. - The program is loaded into
memory. - The program becomes
oneormorerunning processes. - Processes are
typicallyindependent of each other - While threads exists as the
subsetof a process - Threads can talk with each other more
easilythan processes can - Threads are
vulnerableto problems caused by other threads in the same process.